RIRS stands for Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery and is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat kidney stones. It is a relatively new and advanced technique that involves using a small fiberoptic instrument called a ureteroscope to enter the urinary tract through the urethra and then advancing it through the bladder and up into the ureter and kidney.
During the procedure, the surgeon uses the ureteroscope to locate the kidney stone and then uses small instruments, such as lasers, to break up the stone into small pieces, which can then be easily removed through the ureteroscope. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, and patients typically go home the same day or the next day.
RIRS has several advantages over other surgical techniques for kidney stones. It is minimally invasive, which means there is less trauma to the body, and patients experience less pain and a quicker recovery time. Additionally, RIRS can be used to treat stones of all sizes and types, including complex stones that may not be treatable with other techniques.
However, like any medical procedure, RIRS also has risks and potential complications, such as bleeding, infection, and injury to the urinary tract. It is important to discuss the benefits and risks of RIRS with your healthcare provider to determine if it is the right treatment option for you.
How kidney stones are removed ?
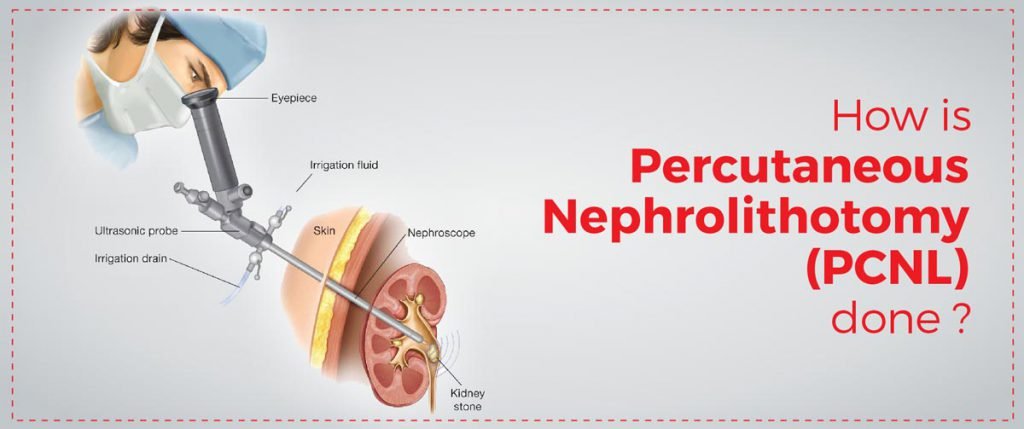
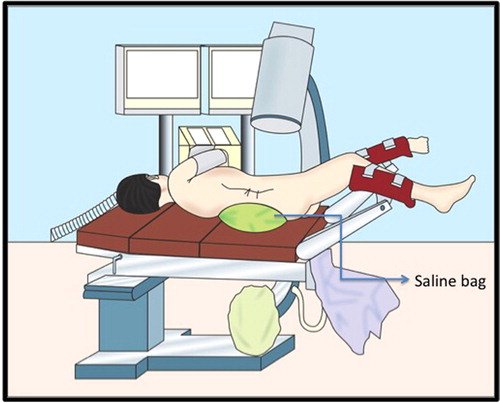
However, it’s worth noting that the choice of surgical approach will depend on several factors, including the size, location, and type of kidney stone, as well as the patient’s overall health and medical history.

