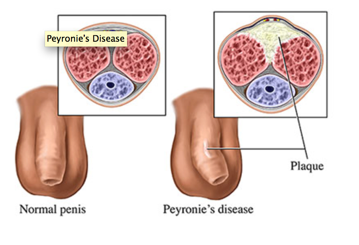
Peyronie’s disease is a condition that affects the penis, causing the development of fibrous plaques within the penile tissue. This can result in curvature, pain, and potential difficulties with sexual activity. While Peyronie’s disease can be distressing, understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, exploring treatment options, and seeking support can help individuals effectively manage this condition. In this article, we will delve into the details of Peyronie’s disease and provide valuable insights for those affected.
Keywords: Peyronie’s disease, penile curvature, fibrous plaques, penile pain, sexual difficulties
Understanding Peyronie’s Disease:
Peyronie’s disease is characterized by the formation of fibrous plaques, or scar tissue, within the penile tissue. These plaques can cause the penis to develop a significant curvature or indentation, leading to pain and potential difficulties with sexual intercourse.
Causes of Peyronie’s Disease:
The exact cause of Peyronie’s disease is not fully understood, but the condition is believed to result from a combination of genetic predisposition, trauma or injury to the penis, and inflammation. Risk factors such as advancing age, family history, and certain connective tissue disorders may also contribute to its development.
Symptoms of Peyronie’s Disease:
The primary symptoms of Peyronie’s disease include:
- Penile curvature: Development of a noticeable curve or bend in the penis, which may be upward, downward, or sideways.
- Penile pain: Discomfort or pain during erection or sexual activity due to the presence of fibrous plaques.
- Erectile dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection due to the structural changes in the penis.
- Penile deformity: Indentations, lumps, or narrowing of the penis as a result of the fibrous plaques.
Treatment Options for Peyronie’s Disease:
- Non-surgical options:
Medications: Some medications, such as collagenase clostridium histolyticum, may be prescribed to break down the fibrous plaques.
Penile traction therapy: This involves the use of devices to gently stretch the penis, promoting tissue remodeling and potentially reducing curvature.
2. Surgical options:
- Penile plication: Involves the shortening of the unaffected side of the penis to straighten the curvature.
- Penile grafting: Utilizes grafts to replace the scarred tissue and restore penile alignment.
- Penile prosthesis: In cases of severe curvature or erectile dysfunction, implanting a penile prosthesis may be considered.
- Excision and grafting: Involves removing the plaque and replacing it with grafts to restore penile shape.
- Support and Coping: Living with Peyronie’s disease can be emotionally challenging. It is essential to seek support from healthcare professionals, as well as from loved ones or support groups. Supportive counseling or therapy can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of the condition, maintain healthy relationships, and manage any anxiety or depression that may arise.
Conclusion:
Peyronie’s disease can significantly impact an individual’s physical and emotional well-being. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, exploring treatment options, and seeking support are key to effectively managing this condition. By working closely with healthcare professionals, staying informed, and accessing available resources, individuals with Peyronie’s disease can navigate the challenges and pursue appropriate treatment strategies to improve their quality of life and maintain healthy relationships.