Blood In Urine
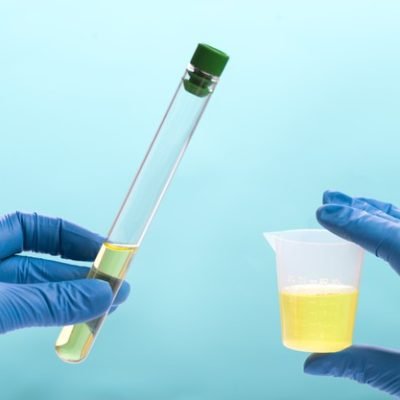
If you see blood in your urine, with or without symptoms of cystitis, you should contact your Doctor immediately for further advice
Your Doctor will normally investigate blood in the urine urgently.
You may be started on antibiotics to treat a presumed infection. However, if the urine test result comes back showing no evidence of infection, you must consult a urologist for more detailed investigations.
What are the facts about blood in the urine?
the commonest cause of blood in the urine is infection (cystitis)
Hematuria can be visible to naked eyes or can be seen as microscopic in urine analysis
Both forms should always be investigated no matter what.
any blood in urine after the age of 40 in both male or female and at any age in smokers should be evaluated to rule out urinary tract cancer.
1 in 5 adults with visible blood in the urine and 1 in 12 adults with non-visible blood in the urine are subsequently discovered to have bladder cancer
children with blood in the urine rarely have cancer – they usually have an infection in the bladder or inflammation of their kidneys (nephritis)
some drugs (e.g. rifampicin, nitrofurantoin) and foodstuffs (e.g. beetroot) can turn the urine red; therefore a proper history of drug intake is important in evaluation.
Causes
What could have caused the blood in my urine?
50% (half) of patients with visible blood in the urine will have an underlying cause identified but, with non-visible blood in the urine, only 10% will have a cause identified
Although there are many potential causes for blood in the urine, those most often identified are:
bladder infection
cancers of the bladder (pictured), kidney or prostate
stones in the kidneys or bladder
inflammation of the kidneys (nephritis)
urinary tract injuries
blood disorders (e.g. sickle cell disease, clotting disorders, anticoagulant and anti-platelet drugs)
other causes, including less common infections (e,g. TB, schistosomiasis)
Evaluation
The usual tests performed are:
a. General blood tests
CBC
KFT
RBS
PSA in Men
b. Urine Analysis
this may show the presence of RBCs in urine along with pus cells if the infection is present.
c. Other specific tests
Urine Cytology for Malignant cells
ultrasound scan KUB Region
CT scan of your abdomen
Specialized evaluation:
Examination under anaesthesia
