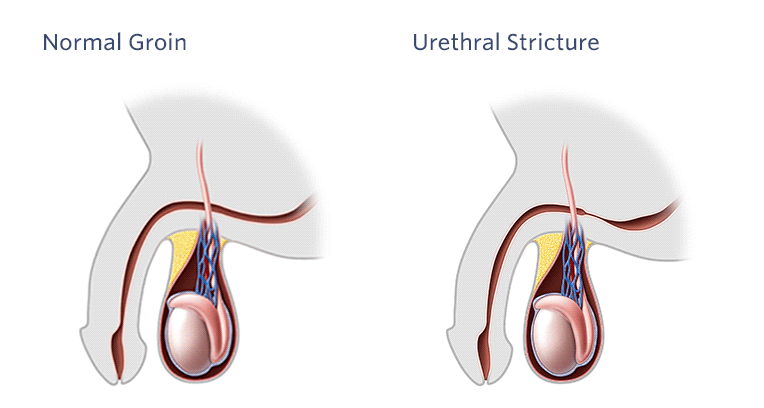
The narrowing of the urethra, medically referred to as “Urethral Stricture” is a significant health concern that can affect both men and women. This condition involves a constriction or narrowing of the passage through which urine exits the body. It not only causes discomfort but can also have a substantial impact on an individual’s quality of life.
Causes of Urethral Narrowing:
Infections and Inflammation: Infections or inflammation in the urethra can lead to scarring and narrowing. Swelling and tissue damage around the urethra can result in a decreased urinary flow.
Urethral Stricture: Urethral stricture refers to the narrowing of one or more sections of the urethra, often due to scar tissue from injury, infection, or other underlying issues.
Urethral Stones: Urethral stones, also known as urethral calculi, can develop within the urethra and cause narrowing. These stones can obstruct the urinary flow and contribute to the constriction of the urethra.
Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma or injury to the pelvic region can cause scarring and narrowing of the urethra, making it difficult for urine to pass through.
Symptoms:
Difficulty Urinating: The most common symptom of urethral narrowing is difficulty urinating and a reduced urine flow.
Painful Urination: Individuals with urethral narrowing often experience pain or discomfort while urinating.
Frequent Urge: Some individuals may feel a frequent urge to urinate, even if the amount of urine passed is minimal.
Blood in Urine: Blood in the urine, known as hematuria, can occur due to the irritation and inflammation caused by urethral narrowing.
Treatment and Management:
Seeking medical attention is crucial if someone suspects they have a urethral stricture. A healthcare provider will assess the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options. Treatment may involve:
Medications: In some cases, medications can help reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
Dilation: This procedure involves inserting a catheter or other devices into the urethra to widen the narrowed section.
Urethral Stent: A stent can be placed in the urethra to keep it open and maintain a normal urinary flow.
Surgery: Surgical procedures can be considered to remove or bypass the narrowed area of the urethra.
Precautions:
Ignoring symptoms of urethral narrowing can lead to complications. Seeking timely medical advice is essential.
If someone notices blood in their urine or experiences severe pain while urinating, they should consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Leaving urethral narrowing untreated can worsen the condition and negatively impact an individual’s health.
Conclusion:
Urethral narrowing is a serious condition that requires medical attention. With the right treatment and care, it is possible to manage and alleviate the discomfort caused by this condition. If anyone suspects they are experiencing symptoms of urethral narrowing, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. Early intervention can help maintain a good quality of life and prevent complications.
